Lung Operation Procedure: A Comprehensive Guide
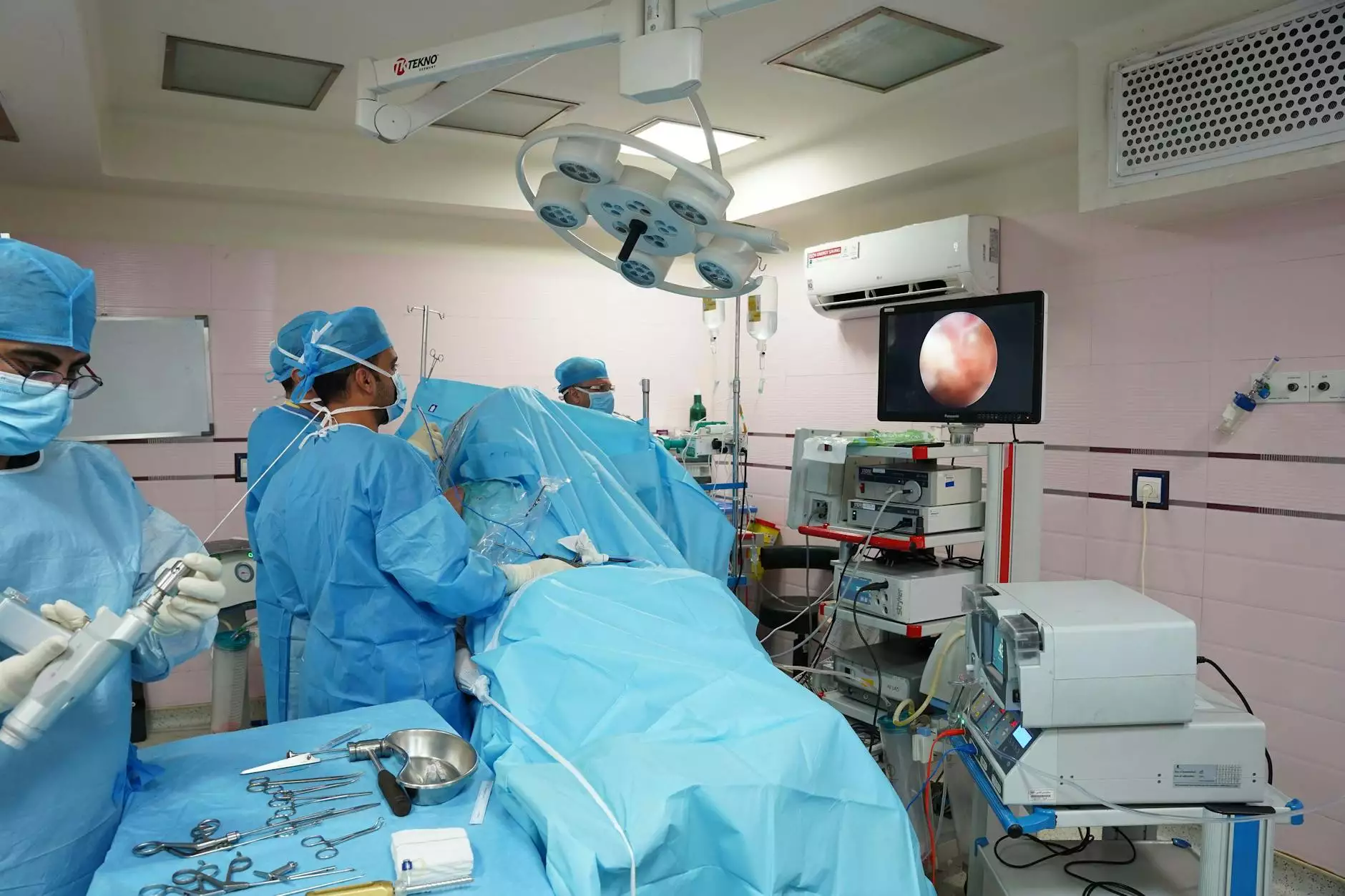
The field of medicine has made significant advancements over the years, particularly in the realm of surgical procedures. One area that has seen remarkable development is the lung operation procedure. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of various lung surgeries, their purposes, procedures involved, and the recovery process, ensuring patients and their families are well-informed.
Understanding Lung Operation Procedures
Lung operation procedures, often referred to as thoracic surgeries, are performed to treat a wide range of lung-related conditions. These surgeries can be necessary for treating lung cancer, emphysema, pneumonia, or various benign conditions. Understanding the types of procedures available is the first step in navigating lung health.
Types of Lung Operation Procedures
- Lobectomy: This is the surgical removal of a lobe of the lung. It is commonly performed for patients with lung cancer.
- Pneumonectomy: This involves the complete removal of a lung. Typically indicated in advanced lung disease or severe infections.
- A segmentectomy involves the removal of a larger segment of the lung, usually for localized tumors.
- Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS): A minimally invasive technique allowing surgeons to access the chest cavity through small incisions with the help of a camera.
- Bronchoscopy: A procedure that allows direct visualization of the airways and lungs, often used for diagnosis and treatment.
- Thoracotomy: An open chest surgery that provides access to the lungs and other thoracic organs.
Indications for Lung Operations
The choice to undergo a lung operation procedure is usually based on specific indications related to the patient's health. Below are some common reasons for these surgical interventions:
- Diagnosis: Lung surgeries may be performed to obtain tissue samples for diagnostic purposes, especially in cancer cases.
- Treatment of Lung Cancer: Surgery is often necessary to remove cancerous tumors and surrounding tissue.
- Treatment of Chronic Diseases: Conditions such as emphysema may require surgical intervention when other treatment options have failed.
- Infection Control: Severe lung infections that do not respond to antibiotics may necessitate surgery to remove infected tissue.
The Lung Operation Procedure: What to Expect
Preparing for a lung operation procedure can be anxiety-inducing. However, understanding the steps involved can greatly alleviate concerns. Below is a breakdown of what patients can expect:
Pre-Operative Preparation
- Consultation: A thorough consultation with the surgeon is essential. This includes medical history evaluation, physical examinations, and necessary imaging like X-rays or CT scans.
- Pre-operative Tests: Blood tests and pulmonary function tests may be conducted to assess the patient's fitness for surgery.
- Medication Management: Patients may need to adjust current medications, discontinue blood thinners, or start new medications as advised by the healthcare provider.
- Smoking Cessation: Those who smoke are generally advised to quit at least several weeks before surgery to improve recovery chances.
- Arrival on Surgery Day: Patients should arrive at the surgical center with time to spare, bringing all necessary documents and having a companion available if possible.
The Surgical Procedure
The exact surgical technique used will depend on the type of lung surgery being performed. Here’s what typically occurs during the operation:
- Anesthesia: The patient will be given general anesthesia to ensure they are unconscious and pain-free throughout the procedure.
- Incision: The surgeon will make an incision in the chest wall. The size and location of the incision will depend on the specific procedure being performed.
- Accessing the Lung: The surgeon will carefully separate the ribs to access the lung tissue. Advanced techniques like VATS involve smaller incisions and specialized instruments.
- Removal or Repair: The necessary lung tissue will be removed or repaired based on the type of procedure. Lymph nodes may also be biopsied if necessary.
- Closure: After the procedure is complete, the surgeon will close the incisions with sutures or staples and apply sterile dressings.
Post-Operative Care and Recovery
Understanding the recovery process following a lung operation procedure is crucial for patients and their families. The recovery experience can vary depending on the complexity of the surgery and the patient’s overall health.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
- Monitoring: Patients will be closely monitored in a recovery room to ensure stable vital signs and to address any immediate post-operative complications.
- Pain Management: Adequate pain control is essential. Pain medications will be administered as needed to ensure comfort.
- Respiratory Care: Patients may need assistance with breathing exercises or the use of an incentive spirometer to promote lung expansion and prevent pneumonia.
Long-Term Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from a lung surgery may take weeks to months. Here are vital aspects of post-operative care:
- Gradual Increase in Activity: Patients should gradually increase their activity levels as tolerated. Light walking is often encouraged soon after surgery.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular follow-ups with the surgeon are crucial to monitor healing progress and manage any complications.
- Nutritional Considerations: A balanced diet can aid the recovery process. Patients should focus on nutrient-rich foods to support healing.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: For some patients, participating in a rehabilitation program can enhance lung function and overall recovery.
Potential Risks and Complications
While lung operations can be life-saving, they also carry risks. Understanding potential complications can help in making informed decisions:
- Infection: There is a risk of infection at the incision site or in the lungs.
- Bleeding: Some patients may experience bleeding during or after surgery.
- Respiratory Complications: Issues like atelectasis (collapse of part of the lung) can occur, as well as pneumonia.
- Anesthesia Risks: Patients may face complications related to anesthesia, though these are rare.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the lung operation procedure is vital for patients facing thoracic surgeries. Advanced techniques, a thorough pre-operative assessment, attentive post-operative care, and proactive communication with healthcare providers play crucial roles in successful outcomes. At Neumark Surgery, we prioritize patient education and holistic care. Our team is dedicated to guiding patients through their surgical journey, ensuring that they have the information necessary to make empowered decisions about their lung health.
For further inquiries or to schedule a consultation regarding lung operations, visit neumarksurgery.com.









